You’ve optimized your WooCommerce checkout page, but customers are still leaving before they even add products to their cart.
Table of Contents
According to the Baymard Institute, the average cart abandonment rate stands at 70.19%. That’s a lot of lost revenue, but here’s what most store owners miss – abandonment doesn’t just happen at checkout.
Customers make the decision to leave throughout their entire shopping journey, and your product page is where a huge chunk of those decisions happen.
The product page is where customers ask themselves critical questions: “Is this actually available?” “How many are left?” “When will I get it?” “What if it sells out?”
If your product page doesn’t answer these questions clearly, customers leave to find a store that does.
This guide covers five code-based implementations that use stock visibility and urgency elements to answer customer questions before they ask. We’re focusing on the honest urgency that comes from real inventory data – not manipulative fake scarcity.
Part 2 will cover checkout optimization, trust signals, and friction removal. Total implementation time: 3-4 hours for all five elements.
Stock Level Display with Urgency
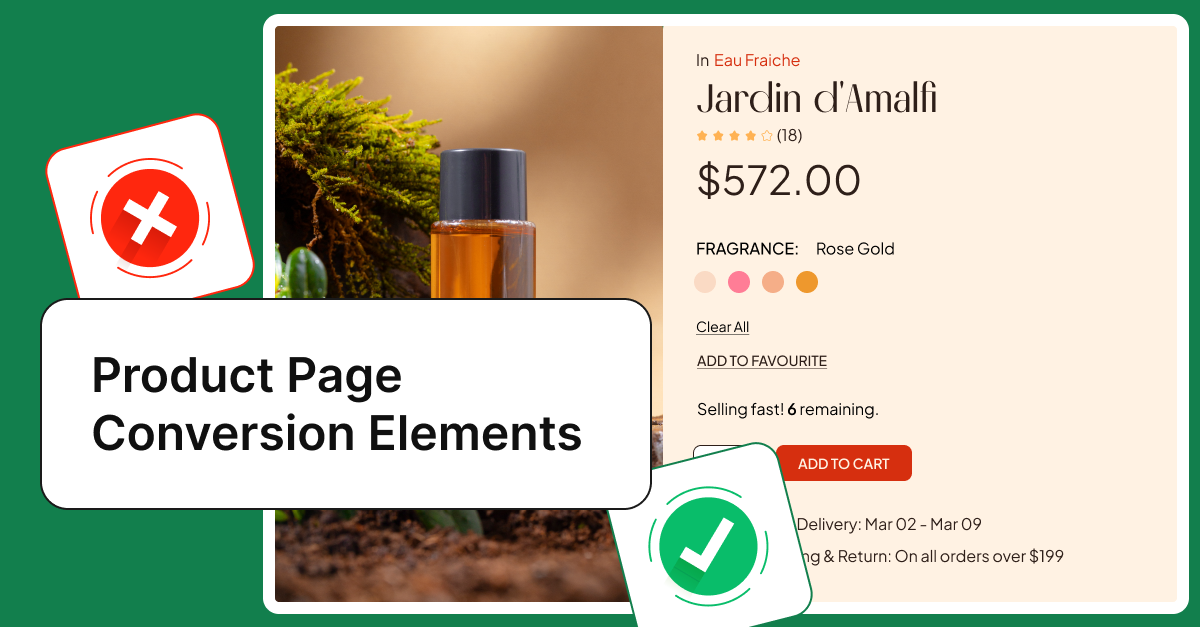
Showing actual stock creates urgency. “Only 3 left” works better than generic “In stock.”
WooCommerce shows stock by default at Settings → Products → Inventory. But you can customize messages based on stock ranges:
// Range-based urgency messages
add_action( 'woocommerce_single_product_summary', 'display_stock_urgency_levels', 25 );
function display_stock_urgency_levels() {
global $product;
if ( ! $product->get_manage_stock() ) {
return;
}
$stock_quantity = $product->get_stock_quantity();
if ( $stock_quantity > 0 && $stock_quantity <= 3 ) {
echo '<div class="stock-urgency critical">🔥 Almost gone! Only ' . $stock_quantity . ' left</div>';
} elseif ( $stock_quantity > 3 && $stock_quantity <= 10 ) {
echo '<div class="stock-urgency high">⚡ Selling fast! ' . $stock_quantity . ' remaining</div>';
} elseif ( $stock_quantity > 10 && $stock_quantity <= 20 ) {
echo '<div class="stock-urgency medium">⏰ Limited stock - ' . $stock_quantity . ' available</div>';
}
}
Three urgency levels: Critical (1-3), High (4-10), Medium (11-20). Adjust ranges based on your sales volume.
Warning: Don’t show urgency for 50+ units. Customers notice fake scarcity.
Custom Stock Status Messages
Generic stock messages don’t tell customers what they need to know. “In stock” could mean “ships today” or “ships in 2 weeks.”
Replace WooCommerce’s default text with contextual messages. “Ships today” vs “Back in stock March 15” vs “2-3 day processing” – each sets different expectations and reduces support questions.
// Customize stock status messages
add_filter( 'woocommerce_get_availability_text', 'custom_stock_messages', 10, 2 );
function custom_stock_messages( $availability, $product ) {
$stock_status = $product->get_stock_status();
// Check if stock management is enabled
if ( $product->get_manage_stock() ) {
$stock_quantity = $product->get_stock_quantity();
// High stock - general availability message
if ( $stock_quantity > 20 ) {
return 'In stock - ready to ship';
}
// Low stock - show specific quantity
if ( $stock_quantity > 0 && $stock_quantity <= 20 ) {
return 'Only ' . $stock_quantity . ' remaining in stock';
}
// Out of stock
if ( $stock_quantity <= 0 ) {
return 'Currently unavailable';
}
}
// For products without stock management, use stock status
switch ( $stock_status ) {
case 'instock':
return 'In stock';
case 'outofstock':
return 'Currently unavailable';
case 'onbackorder':
return 'Available on backorder - ships in 2-3 weeks';
default:
return $availability;
}
}
This filter applies to product pages, shop pages, and cart. Products with 20+ units get “ready to ship,” while 1-20 units show exact quantity.
The backorder message is important – “Available on backorder – ships in 2-3 weeks” sets clear expectations instead of leaving customers uncertain.
Warning: This filter is site-wide unless you add product-specific conditionals. Test on your shop page to ensure messages make sense across all products.
Handling Out-of-Stock Products
When a product sells out, most stores just show “Out of stock” and lose potential sales. Customers who wanted that product either leave or forget about it.
Back-in-stock notifications solve this by capturing customer interest and automatically alerting them when products become available again. The system works through three components:
Email capture form – Displays when products are out of stock, collecting customer emails and product IDs.
Database storage – Stores subscriber information with the products they’re interested in.
Automated notifications – Hooks into WooCommerce stock updates (woocommerce_product_set_stock) to trigger emails when inventory is replenished.
When stock goes from 0 to any positive number, the system queries subscribers for that product and sends notification emails with direct purchase links.
This approach works best for regular inventory products that restock predictably. High-ticket items or custom products often benefit more from personal contact – a simple inquiry form that emails your team instead of automated notifications.
Implementation options:
Want to code it yourself? Our complete guide on sending email when product back in stock covers the full implementation – database schema, form display, email templates, and security considerations.
Or skip the coding and use our free Restock Alerts for WooCommerce plugin. It handles everything – form display, data storage, and automated notifications.
Legal note: GDPR compliance required. Get explicit consent before storing emails, include unsubscribe links, and honor deletion requests.
Tip: Test email delivery to your own inbox first. Check spam folders and test with Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo to ensure notifications actually reach customers.
Custom Product Badges
Visual urgency works differently than text. Badges on product images create immediate impact – customers see them before reading anything.
Badge types that work: Low Stock, Bestseller, New Arrival. Don’t create badges for every attribute – when everything has a badge, nothing stands out.
Critical limitation: Maximum 1-2 badges per product.
Low Stock Badge
// Display low stock badge on shop page
add_action( 'woocommerce_before_shop_loop_item_title', 'display_low_stock_badge', 10 );
function display_low_stock_badge() {
global $product;
if ( ! $product->get_manage_stock() ) {
return;
}
$stock_quantity = $product->get_stock_quantity();
$threshold = 5;
if ( $stock_quantity > 0 && $stock_quantity <= $threshold ) {
echo '<span class="product-badge low-stock-badge">Low Stock</span>';
}
}
Bestseller Badge
// Display bestseller badge
add_action( 'woocommerce_before_shop_loop_item_title', 'display_bestseller_badge', 10 );
function display_bestseller_badge() {
global $product;
$total_sales = get_post_meta( $product->get_id(), 'total_sales', true );
$threshold = 100;
if ( $total_sales >= $threshold ) {
echo '<span class="product-badge bestseller-badge">Bestseller</span>';
}
}
Set your threshold based on sales volume. A store selling 1,000 units monthly might use 100 sales, smaller stores might use 20-30. Show badges on your top 10-20% of products.
Tip: Cache sales queries with transients to avoid repeated database calls on high-traffic pages.
New Arrival Badge
// Display new arrival badge
add_action( 'woocommerce_before_shop_loop_item_title', 'display_new_arrival_badge', 10 );
function display_new_arrival_badge() {
global $product;
$published_date = get_the_date( 'U', $product->get_id() );
$current_date = current_time( 'timestamp' );
$days_threshold = 30;
$days_since_published = ( $current_date - $published_date ) / DAY_IN_SECONDS;
if ( $days_since_published <= $days_threshold ) {
echo '<span class="product-badge new-arrival-badge">New</span>';
}
}
Badge automatically disappears after 30 days – no manual management needed.
Tip: When products qualify for multiple badges, prioritize: 1) Low Stock, 2) Bestseller, 3) New Arrival.
Warning: More than 2 badges per product reduces effectiveness. Badge blindness is real.
Estimated Delivery Date Display
“When will I get it?” is one of the most common customer questions. Most product pages don’t answer it until checkout – by then, many have already abandoned.
Showing delivery dates on the product page reduces anxiety and cuts support questions.
Simple Fixed-Date Approach
Calculate delivery based on fixed processing time plus shipping time.
// Display estimated delivery date on product page
add_action( 'woocommerce_before_add_to_cart_form', 'display_estimated_delivery' );
function display_estimated_delivery() {
// Configuration
$processing_days = 2; // Days to process and ship order
$shipping_days_min = 3; // Minimum shipping days
$shipping_days_max = 5; // Maximum shipping days
$cutoff_hour = 14; // 2:00 PM cutoff for same-day processing
// Get current date and time
$current_time = current_time( 'timestamp' );
$current_hour = date( 'G', $current_time );
// Add extra day if past cutoff time
if ( $current_hour >= $cutoff_hour ) {
$processing_days += 1;
}
// Calculate earliest delivery date
$earliest_delivery = $current_time;
$days_added = 0;
while ( $days_added < ( $processing_days + $shipping_days_min ) ) {
$earliest_delivery = strtotime( '+1 day', $earliest_delivery );
// Skip weekends
$day_of_week = date( 'N', $earliest_delivery );
if ( $day_of_week < 6 ) { // Monday = 1, Sunday = 7
$days_added++;
}
}
// Calculate latest delivery date
$latest_delivery = $current_time;
$days_added = 0;
while ( $days_added < ( $processing_days + $shipping_days_max ) ) {
$latest_delivery = strtotime( '+1 day', $latest_delivery );
// Skip weekends
$day_of_week = date( 'N', $latest_delivery );
if ( $day_of_week < 6 ) {
$days_added++;
}
}
// Format dates
$earliest_date = date( 'M j', $earliest_delivery );
$latest_date = date( 'M j', $latest_delivery );
// Display delivery estimate
echo '<div class="estimated-delivery">';
echo '<strong>Estimated Delivery:</strong> ' . $earliest_date . ' - ' . $latest_date;
echo '</div>';
}
This hooks into woocommerce_before_add_to_cart_form, placing the estimate above the Add to Cart button.
The function sets processing days, shipping days, and cutoff time. Orders after 2 PM get an extra processing day.
It loops through days, skipping weekends. Only business days count toward delivery.
For holiday exclusions:
$holidays = array( '2025-12-25', '2025-12-26', '2026-01-01' );
$date_string = date( 'Y-m-d', $earliest_delivery );
if ( in_array( $date_string, $holidays ) ) {
$earliest_delivery = strtotime( '+1 day', $earliest_delivery );
}
Dynamic by Shipping Zone
For significantly different delivery times by location:
$customer = WC()->customer;
$shipping_country = $customer->get_shipping_country();
$delivery_times = array(
'US' => array( 'min' => 3, 'max' => 5 ),
'CA' => array( 'min' => 5, 'max' => 7 ),
'default' => array( 'min' => 10, 'max' => 14 ),
);
if ( isset( $delivery_times[ $shipping_country ] ) ) {
$shipping_days_min = $delivery_times[ $shipping_country ]['min'];
$shipping_days_max = $delivery_times[ $shipping_country ]['max'];
} else {
$shipping_days_min = $delivery_times['default']['min'];
$shipping_days_max = $delivery_times['default']['max'];
}
Only use this if you have significantly different timelines by zone (domestic vs international, multiple warehouses).
Plugin Alternative
For complex scenarios with multiple variables, Order Delivery Date for WooCommerce handles zone calculations, holidays, and carrier integrations better than custom code.
Tip: Under-promise, over-deliver. Add 1-2 buffer days to account for delays.
Warning: Don’t promise dates you can’t consistently meet. One missed estimate damages trust more than no estimate.
Testing Your Implementation
Test thoroughly before going live. Untested code breaks checkout flows and loses sales.
Email Testing
Sign up with your own email using the actual form. Test the complete user flow as customers will experience it.
Check your inbox and spam folder. Programmatically sent emails often land in spam without SMTP configuration.
Test with multiple providers: Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo. Deliverability varies.
Verify all content displays correctly – product names, links, dynamic content. Click every link. Test the unsubscribe function.
Delivery Date Accuracy
Calculate example dates manually and compare to your code output. Test Monday vs Friday orders, before and after cutoff time, weeks with holidays.
Verify weekend skipping works. Friday orders shouldn’t count Saturday/Sunday.
Check holiday exclusions if implemented.
Test different shipping zones if using dynamic approach.
Compare calculated dates to actual fulfillment for your first 10-20 orders. Adjust buffer days if needed.
Part 2 covers checkout optimization, trust elements, and social proof.
Related Resources
- Send Email When Product Back in Stock (Code Snippet) – Complete implementation guide for automated stock notifications